
When we talk about cryptographic security upgrades, not many people know what this is all about. Let us take you through the most significant cryptographic security upgrade in iMessage history – and how it will help you keep your messages secure.

iMessage Upgrades over the years
In 2011, Apple launched iMessage and provided end-to-end encryption messaging to the masses by default. Over the years, Apple upgraded iMessage’s cryptography and most recently, in 2019, switched from RSA to Elliptic Curve cryptography. What this did, was to protect encryption keys on device with the Secure Enclave, and made data much harder to extract from devices.
Quick Crash Course on Cryptography
Messaging platforms have always tapped on public key cryptography such as RSA, Elliptic Curve signatures and Diffie-Hellman key exchange. These establish secure end-to-end encrypted connections between devices, and algorithms are based on complex mathematical problems that are too computationally intensive for computers to solve.

Source: Apple
Quantum Computing
With the rise of quantum computing, the security of end-to-end encrypted communications are threatened. Though quantum computers don’t currently exist, robust and well-resourced attackers can already prepare by leveraging the decrease in modern data storage costs to carry out attacks. Attackers can retain today’s encrypted data and retain it till they harness a quantum computer that could decrypt it in future – an attack scenario termed as Harvest Now, Decrypt Later.
To mitigate such risks from future quantum computers, the cryptographic community has been hard at work on developing a post-quantum cryptography (PQC). This encompasses public key algorithms that can keep data secure from known threats posed by future quantum computers.

Source: Apple
PQ3 – What Apple is doing to Protect iMessage Users
Apple rebuilt the iMessage cryptographic protocol to advance end-to-end encryption to ensure that users’ iMessage data is kept encrypted and safe from attackers. PQ3 brings a new post-quantum encryption key that generates locally and transmits to Apple servers as part of iMessage. Tapping on PQ3, iMessage continues to authenticate the sender and verify the Contact Key Verification account key to prevent future quantum computers to attack the system.
Source: Apple
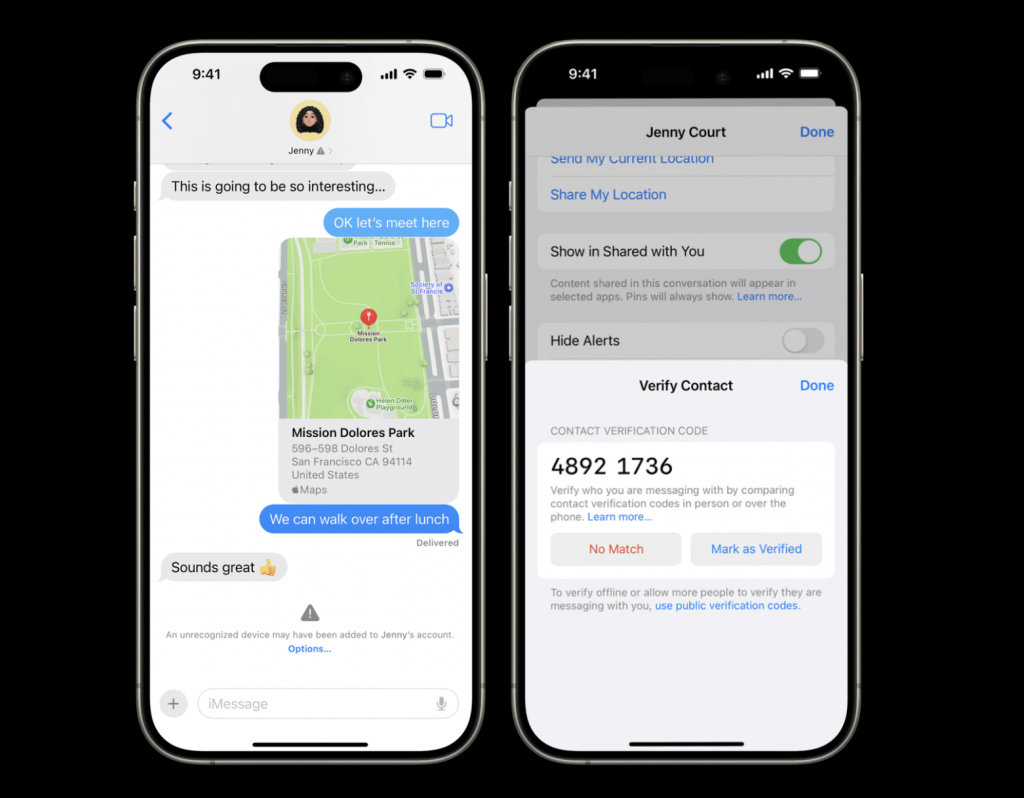
iMessage Contact Key Verification
This will display detected key validation errors in the Messages conversation transcript, and allow users to compare short verification codes to further verify if they are messaging the intended recipient.

Source: Apple
What this means for iMessage users
This protocol will be switched on by default for all devices which are able to update to the latest iOS by the end of the year – so you don’t have to worry that your iMessage data will be accessed by nefarious sources.
Find out more here.






